Applying for a project-based PhD: a user journey map for prospective postgraduate research students
The user journey for students applying for a project-based PhD is distinct from those looking for a self-directed PhD, so we’ve mapped each separately with an accompanying commentary on what we learned from our user research.
In 2023, we undertook research to inform the design of a research degree profile and supporting website content. We’ve already played back our findings to the University’s marketing and student recruitment community, but we wanted to create a journey map to present what we know at a glance.
There are 2 user journey maps for prospective postgraduate research students
The user journey for applying to do a PhD splits according to which type of PhD the applicant is applying for: project-based or self-directed.
To familiarise yourself with this split in the user journey, I recommend you first read my introductory blog post about mapping the prospective research student user journey.
Blog: Our evolving understanding of the prospective postgraduate research applicant user journey
Blog sharing the user journey map for applying to do a self-directed PhD
The project-based PhD applicant journey
The journey for applicants who don’t know how to find and apply for a PhD begins with searching online for opportunities.
There are 3 high-level stages in the user journey
- Stage 1 ‘Awareness’
- Stage 2 ‘Assessment’
- Stage 3 ‘Apply’
Stage 1: ‘Awareness’
The main goals in stage 1 are to find suitable PhD opportunities and to find out about how to apply for a PhD.
Actions and information in Stage 1: ‘Awareness’
Stage 1 can start with either a search for funding or a keyword search for a PhD. Several overseas participants who wanted to study in the UK knew they would need to find funding, so they sometimes began there.
Many participants started with an internet search for a PhD in their desired location or area of research. Some began by looking at highly ranked universities.
Results include a mixture of locations providing information on doing a PhD and advertised PhD projects and research opportunities:
- Ranking websites
- University websites
- Research Centres, Institutes, Departments, Consortia, Funders
- Aggregators like findaphd.com
Participants explored the research opportunities and performed the exact search on aggregator sites.
At this point, they are faced with multiple ways of advertising PhD projects and opportunities, and they gradually learn what options apply to them by exploring the results.
They also sign up to receive regular emails about upcoming opportunities, which again might contain a mixture of different types of PhD.
Emotional journey in Stage 1: ‘Awareness’
Emotions are mixed throughout the process. There is a mix at the start of ambivalence from not knowing what to expect to curiosity and optimism.
In the middle of this stage, the main state is confused. And towards the end, a bit calmer as they find a way to proceed.
Thoughts in Stage 1: ‘Awareness’
Thoughts during this stage reflect a voyage of discovery: learning about PhDs and trying to find a suitable opportunity.
The initial thoughts are about whether to do a PhD and make sense of the options in the search results.
Opportunities in Stage 1: ‘Awareness’
The main opportunity at this stage is to provide clear online information and guidance on the process. This is when people are moving between sections of the website. A clear purpose for what information is published where can help people remember what they read and support them in making decisions.
It is also a time when people are moving between university websites, and clarity of information stands out.
This is also a prime time to feature attraction and engagement content. One participant was so inspired by the video introduction to the research centre that he insisted on playing it for me during the research session.
Stage 2: ‘Assessment’
For project-based PhD applicants, there are 2 further high-level stages in the user journey.
The second stage is ‘Assessment’. The overarching goal in this stage is to review the search results, assess the opportunities and identify suitable projects to apply for.
Actions and information in Stage 2: ‘Assessment’
The applicant will assess their eligibility for an individual project advert and, if qualified, review the centre, school, group or Institute.
They are particularly interested in the working environment. Some participants prioritised this over finding the ‘perfect’ project and were willing to compromise on the project for a good working environment. They were very interested in learning about the supervisor, their publication and track record in research and what they would be like to work for.
All participants looked at the university website in detail to find information, some in very granular detail; for example, a participant examined the supervision history of a potential supervisor, noting any gaps and looking up the publications of their past PhD students. They also looked for opportunities to speak to people and ask detailed questions.
Emotional journey in Stage 2: ‘Assessment’
At the start of this stage, the scale of the work to assess the search results can be daunting, reflected in the middle of the stage. By the end of the stage, participants were less stressed when they found suitable projects to apply to.
Thoughts in Stage 2: ‘Assessment’
Thoughts during this stage are about the project, the work environment and the suitability of the opportunity. In summary:
- Is this the right project for me?
- What is the working environment like?
- What is the supervisor like to work for?
Opportunities in Stage 2: ‘Assessment’
In this stage, the main opportunities are to make it straightforward to locate projects on the University website and to provide information on the working environment and supervisor.
Stage 3: ‘Apply’
Actions and information in Stage 3: ‘Apply’
The goal in this phase is to apply for the chosen project.
For project-based PhDs, the application process can vary and is stipulated in the project advertisement. Variations we encountered:
- Email the lead academic for an informal chat. If successful, submit an online application as the last step
- Email the lead academic to arrange an interview
- Email CV and cover letter to the lead academic
- Submit a comprehensive online application similar to applying for a job
Emotional journey in Stage 3: ‘Apply’
This stage is marked by relief after completing the search and finding an opportunity. Excitement and optimism emerge at the prospect of the outcome, tempered by a bit of apprehension that they followed the correct process.
Thoughts in Stage 3: ‘Apply’
Thoughts here relate to making a good application, in summary:
- Did I follow the correct process?
- Did I make the best application?
- What happens next?
Opportunities in Stage 3: ‘Apply’
Here, opportunities exist to make the application process and communication clear and explicit.
Variations on the user journey
These steps are a common thread for an applicant to a project-based PhD who does not know about the process when they begin. There were notable examples of people taking a shorter route, even though they did not know the whole process.
Finding a project very early on
Applicants who find a project very early on can progress from the start to the end without having to assess multiple options. For example, a participant described their experience of seeing a project in an email newsletter, speaking to the lecturer, who was known to them, emailing their CV and getting the PhD place quite quickly. Others who progressed quickly did so by having a project or PhD programme suggested by an academic or colleague.
Having guidance from an academic
Participants who were advised to do a PhD by an academic often had guidance on what steps to take when, how to prepare a proposal and how to find funding. This shortened and simplified their journey.
Going straight to particular university websites from the start
Overseas applicants who want to study in the UK and know they will need funding might only be able to consider specific universities stipulated by the funding provider. They will also go through a shorter process and might start by directly exploring the university websites.
The project-based PhD user journey map
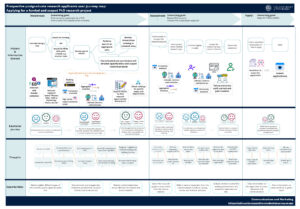
There are 3 high-level stages in the project-based PhD prospective student user journey. Our user journey maps are based on interviews with 20 applicants to the University of Edinburgh.
Download all prospective student user journey map (PDF – University of Edinburgh staff login needed)
More about our prospective student user journey maps
This post is part of a series:



