We’re thrilled to announce the launch of Hidden Heritages, a brand-new website for accessing Scottish and Irish traditional tales. This resource is the outcome of an international, multi-year collaboration between universities in the UK, Ireland and USA, generously supported by the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC) and the Irish Research Council (IRC).
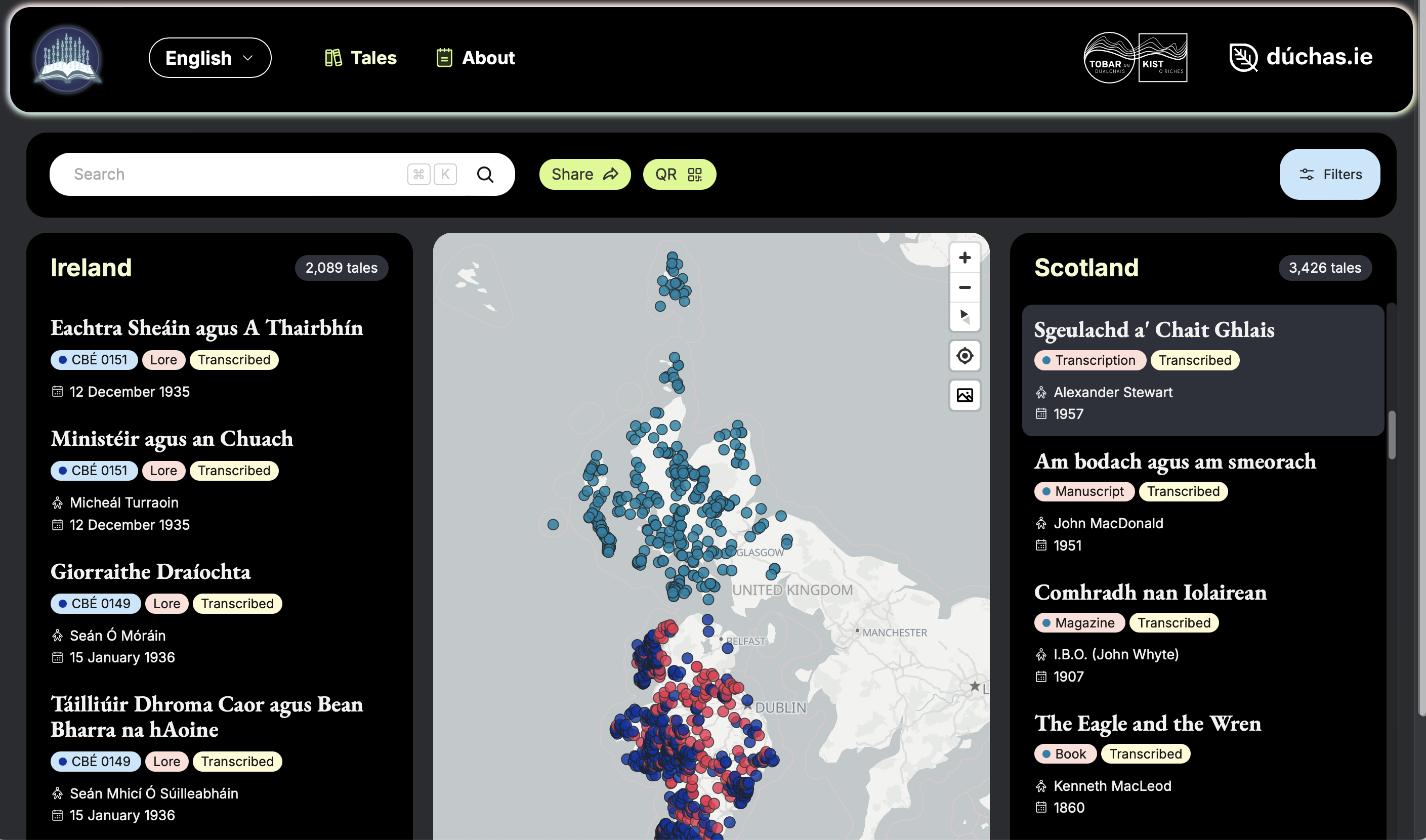
Between 2021 and 2024, our team digitised and recognised thousands of tales from the School of Scottish Studies Archives (SSSA) and the Irish National Folklore Collection (NFC). The result? An online repository featuring 5,515 folktales, with more than 3,400 tales from Scotland and over 2,000 from Ireland.
Behind the Scenes
Many of these tales date back centuries and were collected orally from tradition bearers up to the end of the 20th century. Ethnologists at the SSSA and NFC transcribed thousands of them from fieldwork recordings as handwritten manuscripts. In other cases, the tales came from printed books and articles. Using AI-powered text recognition (OCR for printed material and HTR for handwriting), the research team converted these documents to digital text and have now made them publicly accessible online, often for the very first time. Transkribus, the handwriting recognition tool, was instrumental for this work.
While the automatic transcriptions aren’t flawless, the accuracy is impressive, with less than 5% error rates. And because the original transcriptions often captured rich dialectal forms of Irish and Scottish Gaelic, these texts are a goldmine for linguistic and cultural analysis.
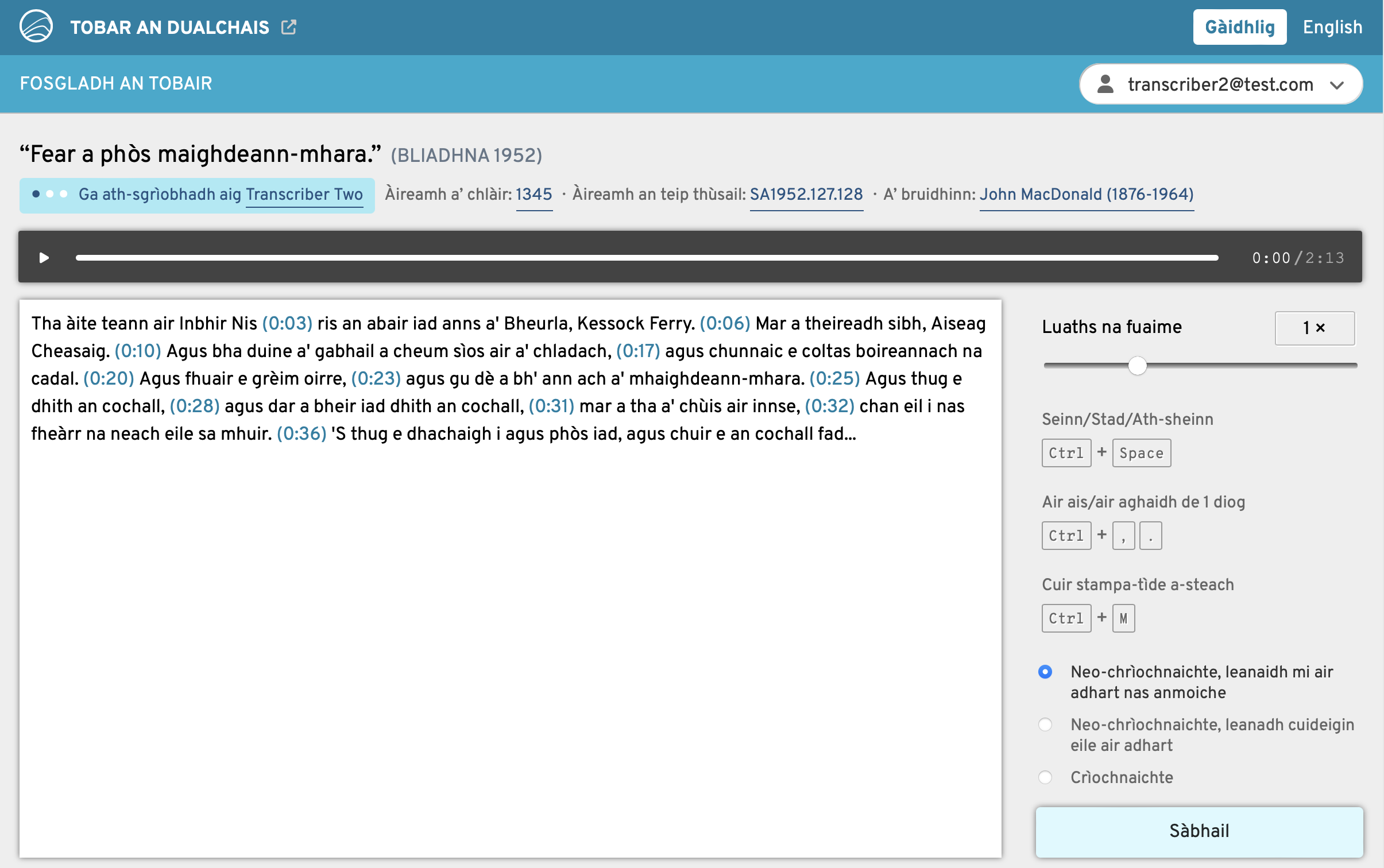
![Image shows metadata, a PDF and AI-recognised text for the Scottish Gaelic tale 'Biast na[n] Naoi Ceann' ['Beast of the Nine Heads']](https://blogs.ed.ac.uk/garg/wp-content/uploads/sites/1179/2025/06/Screenshot-2025-06-05-at-11.14.05.png)
Viewing the texts and metadata for the Gaelic tale ‘Biast na[n] Naoi Ceann’ (‘Beast of the Nine Heads’)
Dall ort! Jump Right In!
Using the website couldn’t be simpler. Explore by searching for your favourite folktale themes. Perhaps you’re interested in tales of witches (buidsichean), giants (fuamhairean) or fairies (Na Daoine Beaga ‘The Wee Folk’). You can filter stories by date, tale-type, language, gender of collectors and narrators, and much more. Interactive visual maps will guide you straight to tales from particular places, letting you discover how stories travelled and evolved.
Users who don’t have Gaelic or Irish can copy and paste texts into Google Translate to get a rough English translation. For many of Scottish tales, we also include direct links to Tobar an Dualchais / Kist o Riches, where users can access the original fieldwork recordings from the School of Scottish Studies Archives. Irish readers can even help to improve some of the transcriptions, but following links to Meitheal Dúchas.
Whether you’re a researcher, folklore enthusiast or just curious about traditional tales, we invite you to explore, share and participate in this rich cultural legacy. Scottish material is provided for research purposes, and Irish stories are available under a Creative Commons licence, allowing non-commercial reuse — remember to attribute your sources carefully.
Visit www.hiddenheritages.ai and explore Gaelic storytelling now! And keep an eye out for our upcoming book, Decoding the Oral Traditions of Scotland and Ireland: From Manuscripts to Models, to be published by Edinburgh University Press in 2026.