New paper in First Monday
We have a new paper that developes the policy report in to an academic paper, exploring the methods, data, theory and implications.
Ben Collier, James Stewart, Shane Horgan, Daniel R. Thomas, Lydia Wilson (2024) INFLUENCE GOVERNMENT, PLATFORM POWER AND THE PATCHWORK PROFILE: EXPLORING THE APPROPRIATION OF TARGETED ADVERTISING INFRASTRUCTURES FOR GOVERNMENT BEHAVIOUR CHANGE CAMPAIGNS, First Monday, Volume 29, Number 2 – 5 February 2024
Abstract
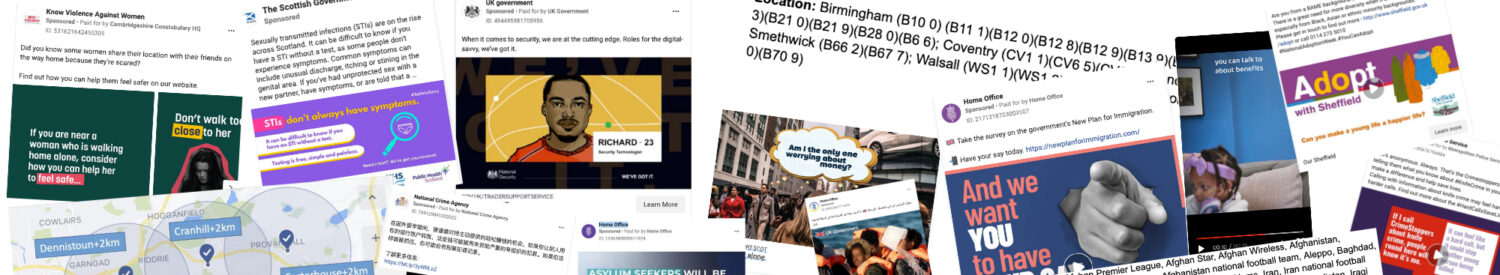
The targeted digital advertising infrastructures on which the business models of the social media platform economy rest have been the subject of significant academic and political interest. In this paper, we explore and theorise the appropriation of these infrastructures — designed for commercial and political advertising — by the state. In the U.K., public sector bodies have begun to repurpose the surveillance and messaging capacities of these social media platforms, along with the influencer economy, to deliver targeted behaviour change campaigns to achieve public policy goals. We explore how frameworks of behavioural government have aligned with Internet platforms’ extensive infrastructures and the commercial ecologies of professionalised strategic marketing. We map the current extent of these practices in the U.K. through case studies and empirical research in Meta’s Ad Library dataset. Although the networks of power and discourse within the ad infrastructure are indeed acting to shape the capacities of the state to engage in online influence, public bodies are mobilising their own substantial material networks of power and data to re-appropriate them to their own ends. Partly as a result of attempts by Meta to restrict the targeting of protected characteristics, we observe state communications campaigns building up what we term patchwork profiles of minute behavioural, demographic, and location-based categories in order to construct and reach particular groups of subjects. However, rather than a clear vision of a ‘cybernetic society’ of reactive information control, we instead find a heterogeneous and piecemeal landscape of different modes of power.