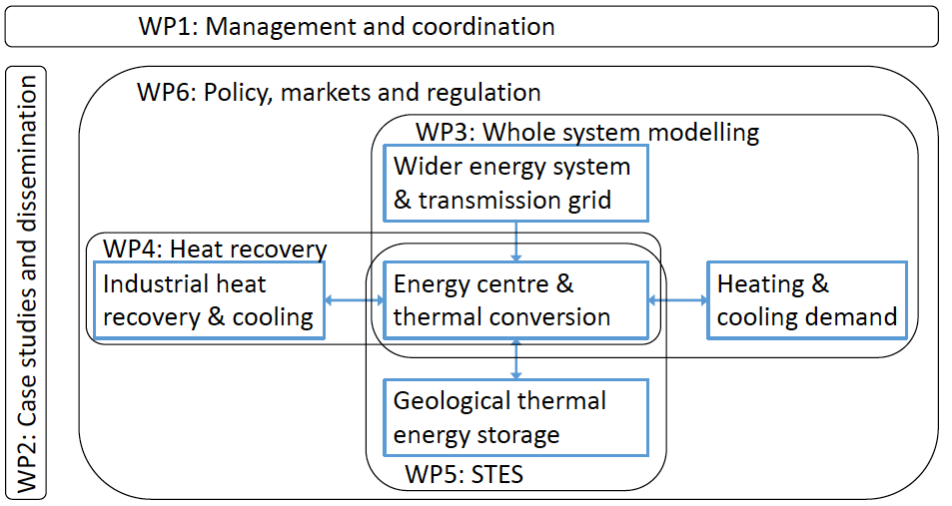
WP1: Management and coordination
The individual work strands will produce novel results but the true value of the project lies in the interplay and coordination between energy supply and demand, storage characteristics and regulation.
WP2: Case studies and dissemination
The full potential of the project can only be reached by combining results from individual work packages. To achieve this, we will bring all researchers together (the PDRAs and investigators will spend significant amounts of time at partner institutions) to develop case studies and guidelines for designing STES as an integral part of a net-zero energy system.
WP3: Whole system modelling and optimisation
This work package will enable STG with STES to be designed and operated as part of the wider energy system to achieve their full potential of reliable, affordable and sustainable thermal energy for consumers and provision of flexibility services for the wider energy system. However, such an integrated system will have multiple energy vectors, multiple stakeholders and complex temporal and spatial interactions which significantly increase the modelling and optimisation complexity.
WP4: Heat recovery and cooling demand
This work package will investigate the potential to match heat recovered from industrial processes with UK heating and cooling demand. We will map the quantity and grade of potential sources of waste heat against current heat recovery technology and this data will inform WPs 3, 5 and 6.
WP5: Seasonal thermal storage
This work package will assess ATES and BTES options to identify the most efficient and resilient solutions, based on the case studies (WP2) and the estimates of thermal energy storage requirements from WP 3-4.
WP6: Policy, markets and regulation
This WP will address how we value the flexibility services provided by the STES system in the wider UK energy system transition context. The need for greater energy system flexibility is identified as a key gap and potential barrier to the achievement of net-zero emissions. The challenge is technical, given the need to maintain national security and quality of supply standards with reduced availability of fossil fuels. It is also a policy challenge as new market and regulatory frameworks need to be designed and implemented to value different forms of flexibility in a way
which contributes to whole system optimisation.