The second week, we were asked to create our curatorial project. At first, I didn’t have a clue. So in class, Beth guided us through the process of finding and exploring “What is a good curatorial project?” Each of our Basho groups was assigned a different example and reading, and we were asked to find a series of curatorial contexts in the given curatorial institutions, such as their goals, values, and visions. And summarize the content to create our own curatorial project.
Initial idea.
My initial curatorial idea was based on the keywords: PLAY, TIME, and HUMAN.
I tried to divide the curatorial exhibition into three stages based on age. Based on Aristotle’s “Three Stages of Educational Development”, the great philosopher and educator in the ancient history of the world.
1.Stage 1: 0-7 years old. Early childhood stage, the game is mainly to develop the child’s body and soul. At this time, children’s games are mainly hands-on games. Such as turnip squats. (Rules: a group of five people, each person to the color or number named radish, there are red, white, yellow, green, purple, five kinds of radish, white radish squatting first, squatting time to read “white radish squatting, white radish squatting, white radish squatting after the red radish squatting.” (The red carrot heard the instruction to repeat the steps of the white carrot and began to squat, after which it continued to specify the next different colors of the radish squat.)
2.Second stage: 7-14 years old. Children’s games are mainly based on emotional (non-rational) education. For example, you draw and I guess. (Rules: groups of two, free combination, two people stand facing each other, according to the host prompt, one person makes an action, and the other person guesses the word. The person in charge of the comparison cannot say any word containing the guessed word)
Purpose: To exercise children’s divergent thinking, and improve children’s teamwork ability, communication ability, and active thinking.
3.Third stage: 14-21 years old. The game is mainly to develop intelligence. For example: wooden block game. (Rules: 6 wooden blocks stacked, the player to ensure the structure of the wooden blocks (wooden blocks do not fall) on the basis of one of the pieces of the draw, in order to pass the level.) This is a game that is both fun and challenging intelligence.
4.Stage 4: Set the age to 60 years old and above. At this point, an hourglass device is shown. On the one hand, I believe that life is a battlefield, everyone must “pass five levels and six generals”, in order to achieve their own life’s ideal continuous efforts. Once people have satisfied the first seven needs of Maslow’s theory, they begin to search for “transcendent needs” – the values of self-realization. (McLeod, 2007) The “hourglass” game device here is an allusion to the Buddhist phrase “all four are empty”. From the Sutra of the Forty-two Chapters: “The Buddha says, “Remember that each of the four great bodies has a name, and none of them has a self.”It means that the elements that make up all things are not real and have no self-nature. On the other hand, it is in line with Schiller’s doctrine of play: so-called play is the impulse of man to take aesthetic appearance as the object, a pure play without utilitarianism and purpose. (Yiying ,2007) In the period of “transcendental needs”, human beings are like an hourglass, passing by with time and following the nature of the world.

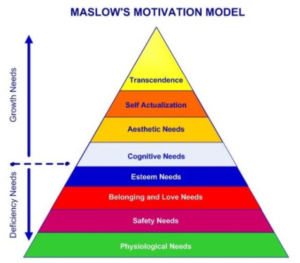
I associate the three keywords PLAY, TIME, and HUMAN together. The reason is that I think life itself is a game. Each of us is the main character in our own game. And society is also a game, people can only achieve the “ideal” society by cooperating with each other.
Reference
1.McLeod S. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs[J]. Simply psychology, 2007, 1(1-18).
2.Guo Yiying. A test of Schiller’s “game theory”[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University: Philosophy and Social Science Edition, 2007 (S1): 226-


Leave a Reply