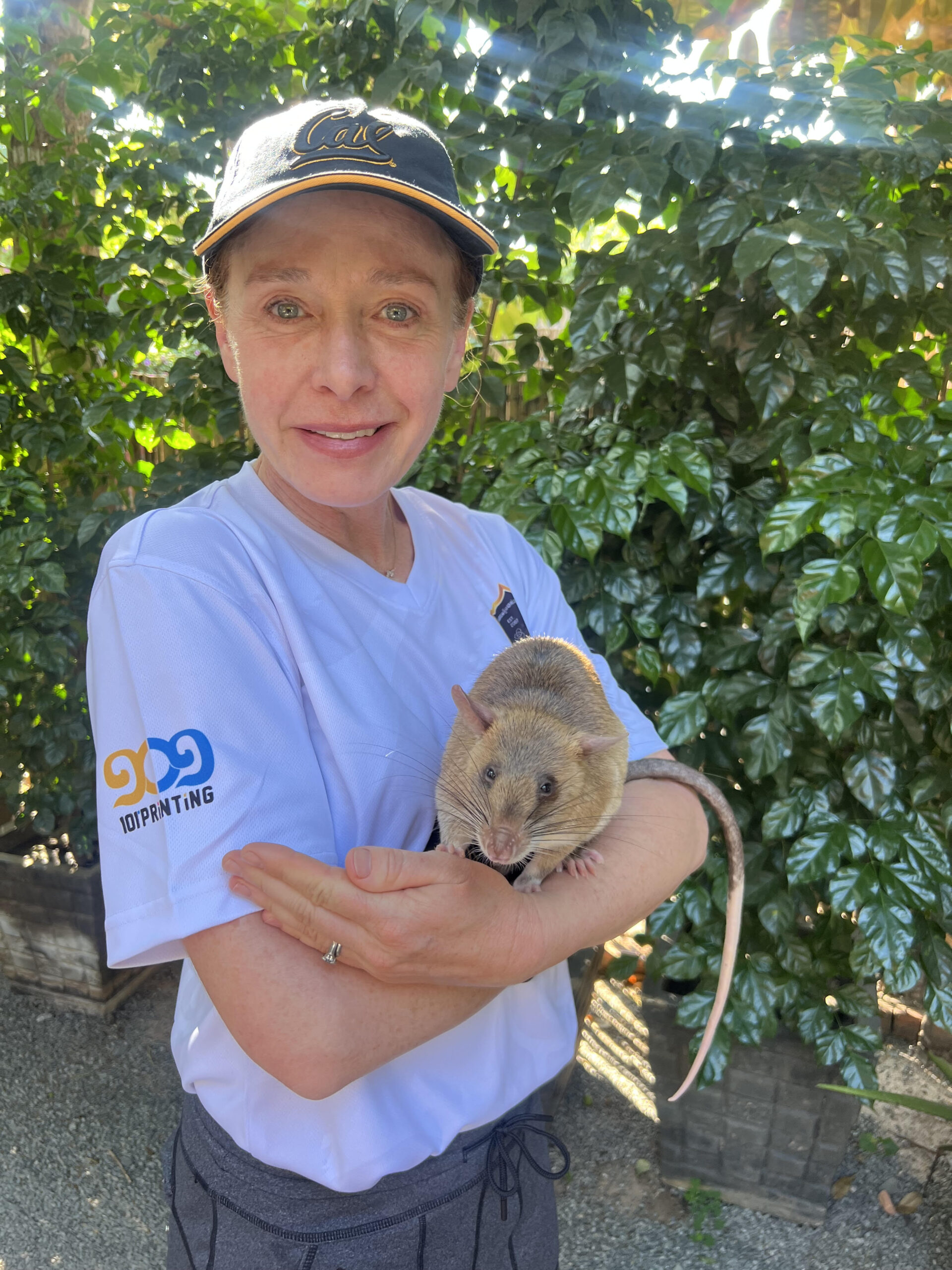
In this blog post, one of our One Health alumni shares insights into her incredible journey from a business oriented career, in Silicon Valley, into One Health. Whitney Hischier graduated from the One Health MSc programme in 2024 after completing a dissertation project focussed on working dogs, entitled “Scent Detection Dogs in the US: Uses and Challenges”. This fascinating project has since seen Whitney take on a role with the the incredible organisation APOPO, a charity training HeroRATs and HeroDOGs to use their extraordinary sense of smell to detect landmines and deadly diseases, including tuberculosis. In doing so, they are saving lives and restoring hope in communities across the globe.
From Silicon Valley to rural Tanzania: my journey into the world of animal scent detection
I entered the MSc in One Health programme as a bit of an outsider as someone who is on the Business School faculty at University of California Berkeley and had no formal education in the veterinary world. I had discovered the field of One Health during the pandemic, when suddenly zoonotic disease became a household term, but my childhood desire to become a vet had been derailed by a poor mark in organic chemistry at university. With this desire reignited in me and knowledge that everyone can find a home in and contribute to One Health, I applied and was not disappointed.
I loved the MSc programme and carried this passion into my final dissertation year. My chosen research topic for the dissertation grew out of a meta-level question of ‘what can animals do that technology cannot?’ – a pertinent question perhaps given that I live in the techno-centric world of Silicon Valley.
This led me to the world of animal scent detection, specifically with dogs and how the market for these specialised dogs has developed in the United States. The One Health programme team connected me with a fantastic mentor, Cindy Otto, who runs the Working Dog Center at University of Pennsylvania’s vet school setting me up for my dissertation year. This turned into a fascinating exploration of the work of stakeholders in the working dog world, with work briefs ranging from explosives detection and police work to wildlife and disease detection.
During this time, I was also travelling to Cambodia frequently to help run a joint USAID – UC Berkeley programme. Whilst there, I visited the APOPO Visitor Centre in Siem Reap. APOPO is an incredible organisation who employ African pouched rats (Cricetomys ansorgei) as well as dogs for land mine detection, tuberculosis detection, search and rescue and wildlife smuggling. APOPO operate in a number of countries, though much of the mine-action work is in Cambodia, a vestige of the Khmer Rouge era.

To appreciate just how incredible this collaborative work is it helps to understand how rats go about surveying a field, connected by via a harness to a line the length of the survey area: When they detect the volatile organic compounds (VOC) of an explosive, they scratch and are immediately given a food reward. These “HERORats” can search an area the size of a tennis court in thirty minutes; by contrast a human deminer with a metal detector can take up to four days to cover the same area. The rats work in conjunction with technical survey dogs who search larger areas of difficult terrain with high levels of vegetation.
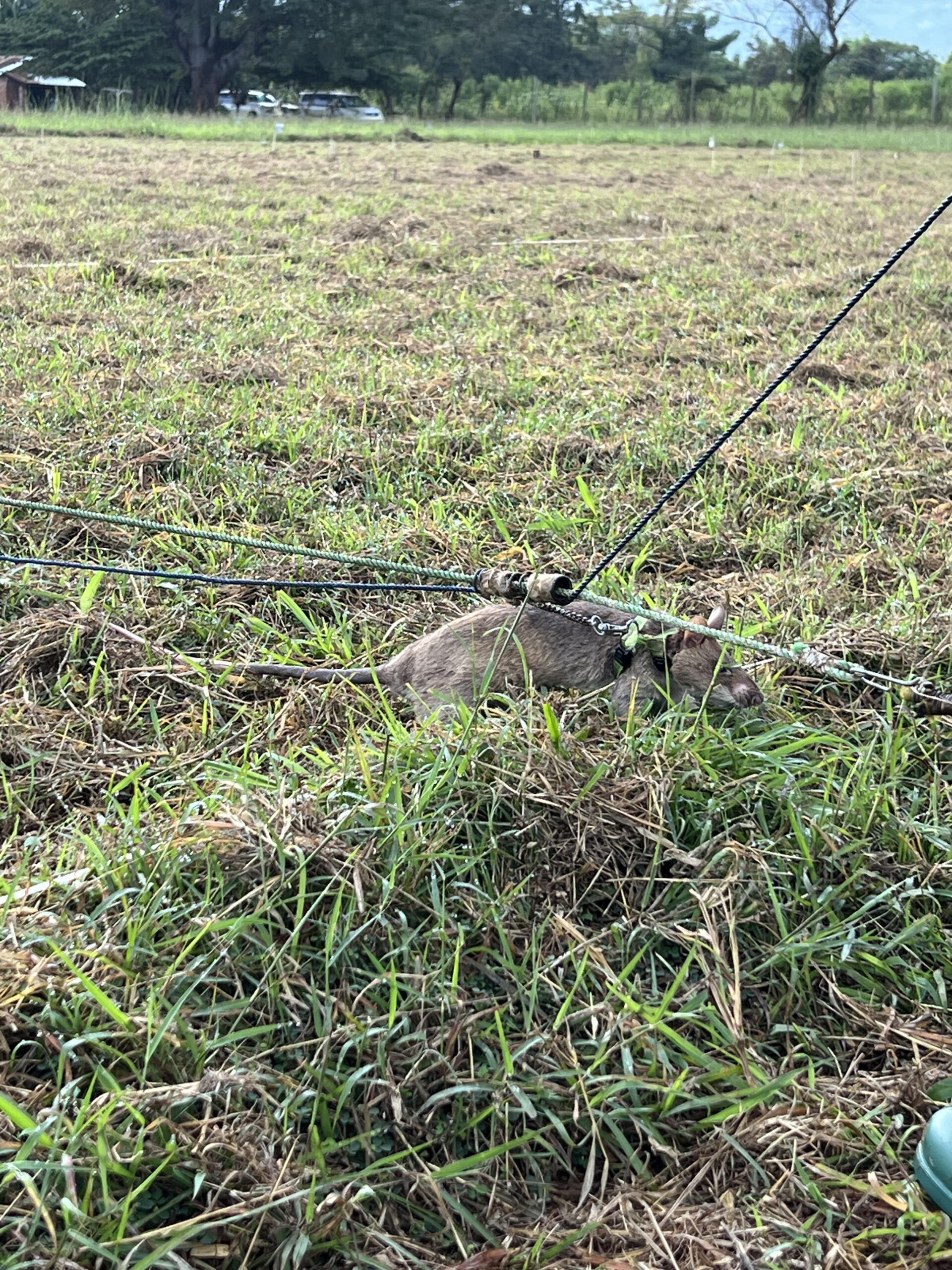

Impressed by their work, I found myself reaching out to APOPO to see how I could help and very soon was involved. It started with overseeing research projects with my students and has since developed into taking up a position on their US board. I have seen at first hand some of their work across the world:
In February, I visited an active mine field outside of Siem Reap, where APOPO is working to de-mine between a series of temples, part of a UNESCO Heritage site. Then, in June, I travelled to Sokoine University of Agriculture (SUA), in Morgoro, Tanzania where APOPO breeds and trains their rats. The trip included a visit to the tuberculosis (TB) lab where the rats are detecting TB in samples from local clinics, as well as to the cargo area of the Dar es Salaam airport, where the rats inspect packages for trafficked wildlife parts (no photos were allowed but it was amazing to see the rats detect tiny amounts of giraffe pelt in a massive, heavily packaged box).
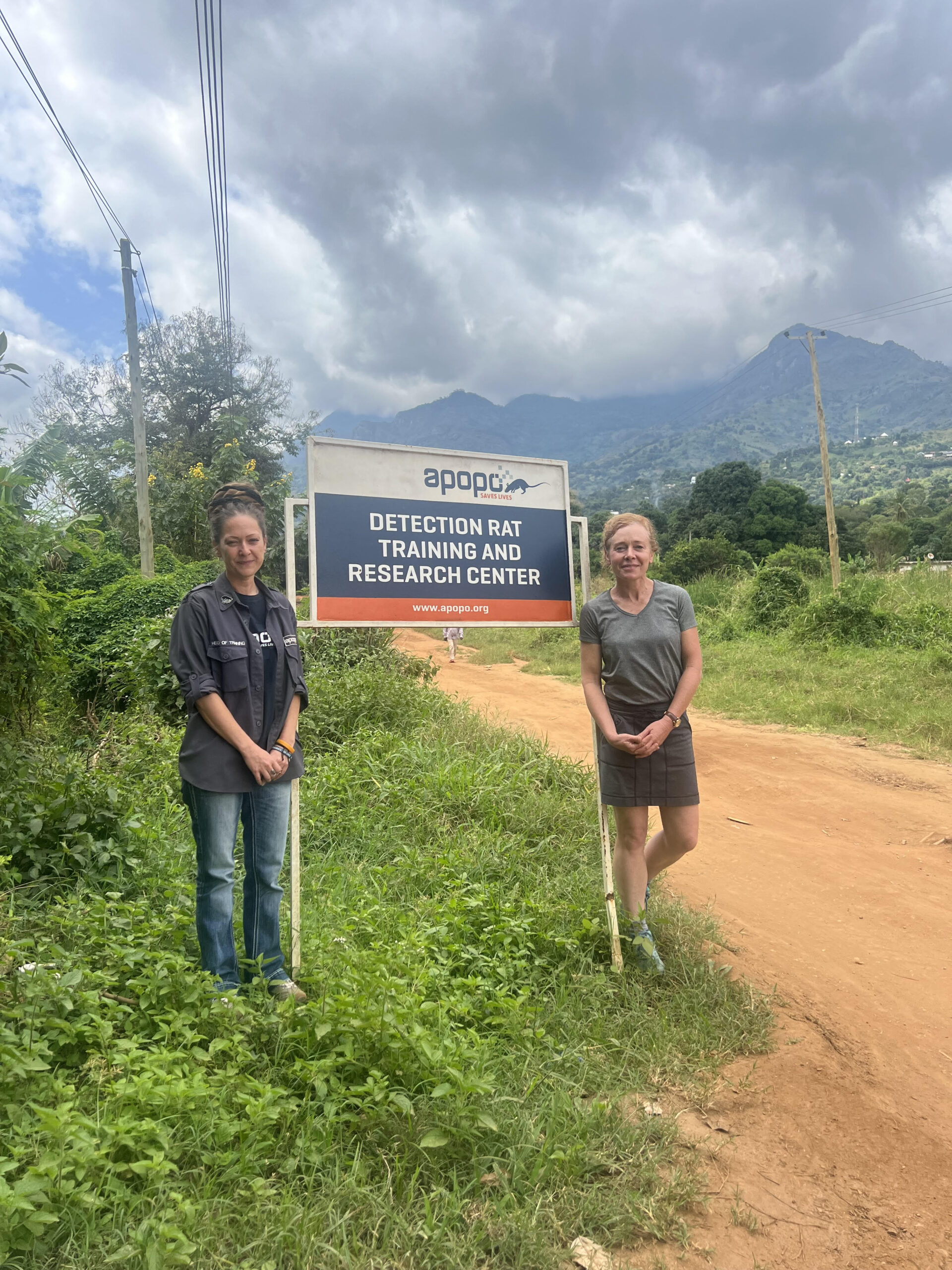

My journey from the One Health MSc programme to APOPO was not one I would have ever predicted. While technology may surpass animal scent detection capabilities at some point, I am excited to be part of an organisation that is constantly finding new ways that dogs and rats can synergistically work with people to combat some of the larger societal challenges we face, including both disease and weapons.
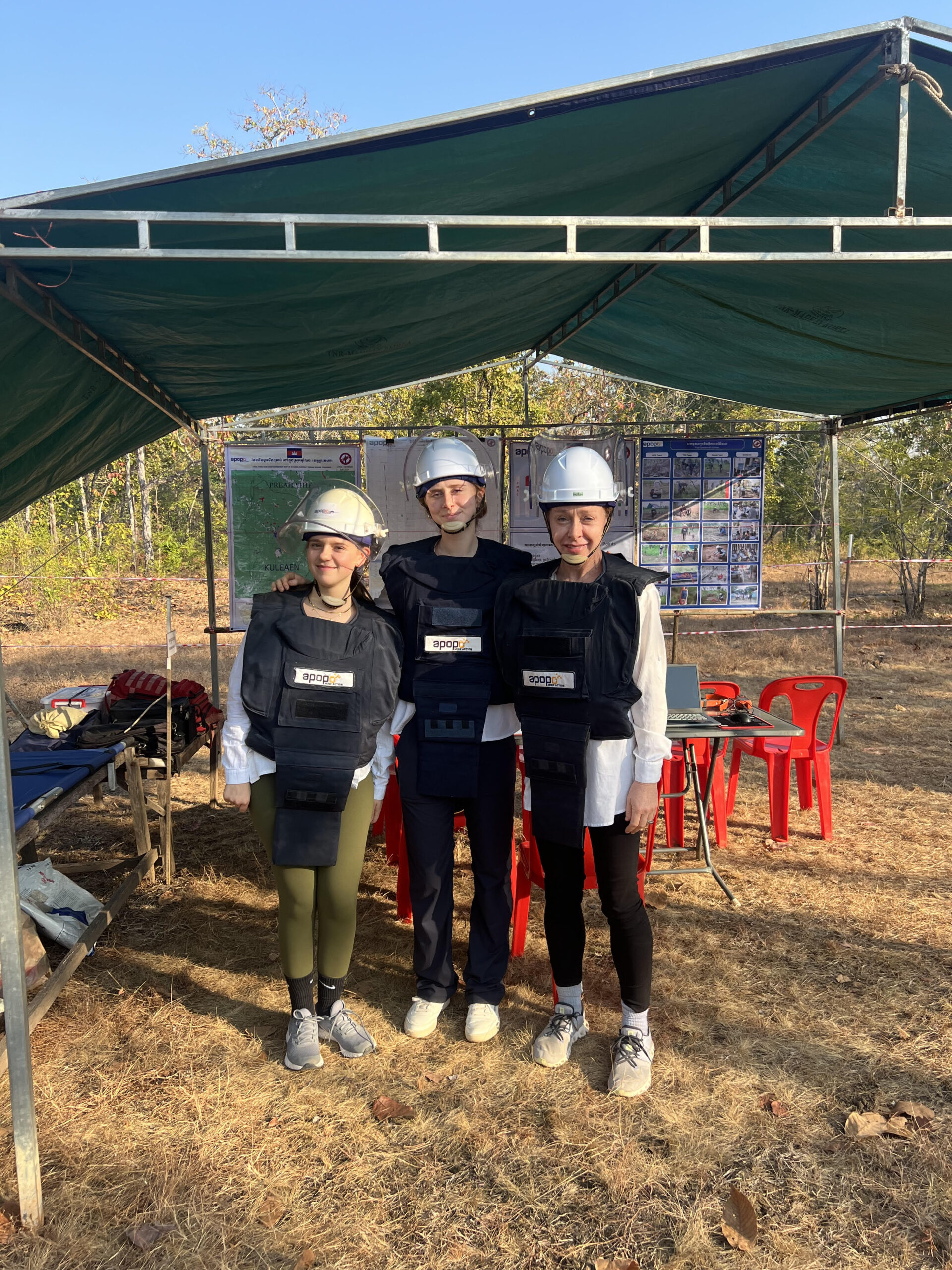
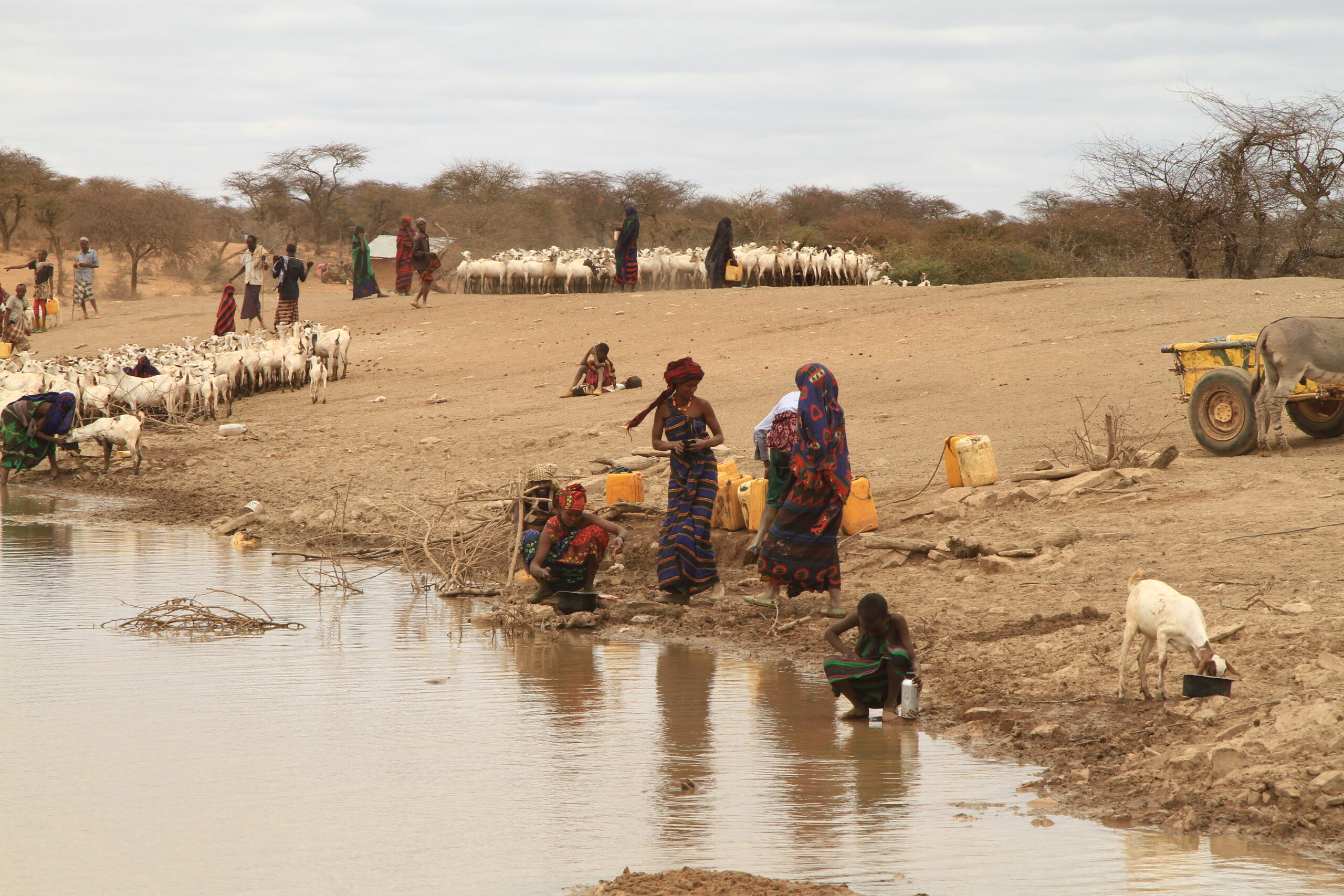
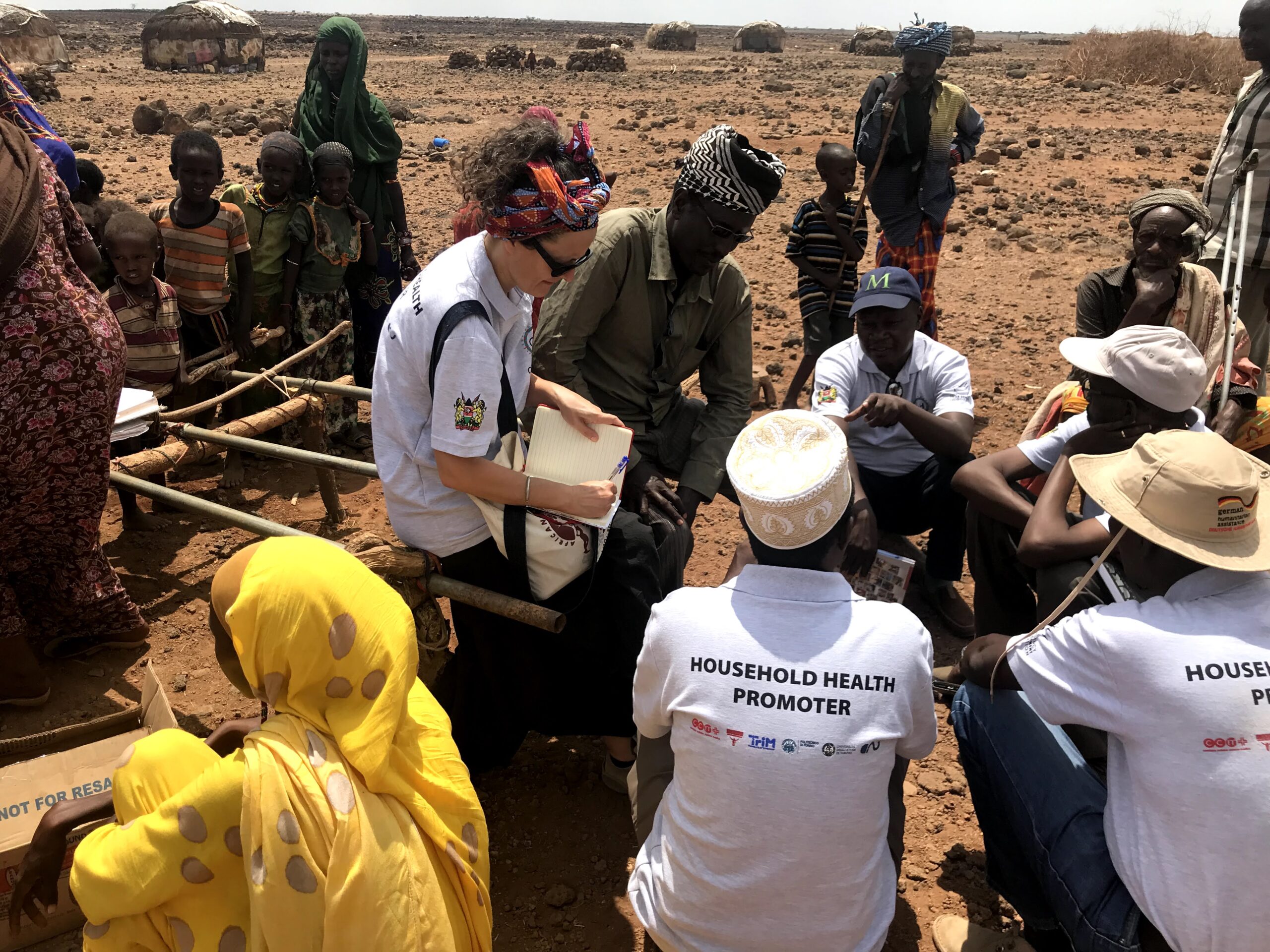




























 Figure 2: The author tending to a traumatised orphan rhino
Figure 2: The author tending to a traumatised orphan rhino
