In order to achieve the functions of distance measurement and wireless data transmission at the same time, we finally chose the solution of connecting the ultrasonic sensor using M5StickC Plus. In terms of hardware connection, the VCC, GND, and SIG pins of the Grove ultrasonic sensor are connected to 5V, GND, and GPIO 26 of the M5StickC Plus, respectively.

In actual operation, the ultrasonic sensor is responsible for measuring the distance between the two devices, and the M5StickC Plus reads the distance measurement results and sends them to the computer via UDP protocol and Wi-Fi. The computer runs a Python-based programme that receives the UDP data from the M5StickC Plus, converts it into OSC compliant data, and then transmits it to the Max/MSP patch for interactive control.
15/03/2025
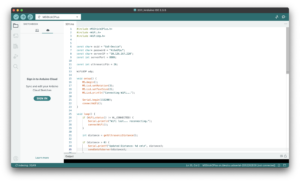
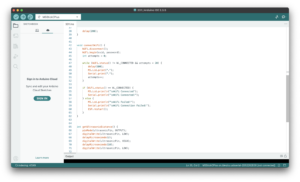
In actual development, I first wrote and uploaded an Arduino programme for the M5StickC Plus to read the distance data from the Grove ultrasound sensor and transmit it wirelessly to the computer. Wireless transmission is based on the devices being connected to the same Wi-Fi network and communication is accomplished by setting the IP address of the host computer.
Once the data could be transferred, I made certain optimisations according to the actual situation: – Disconnection detection and automatic reconnection: when the Wi-Fi connection is interrupted, the M5StickC Plus screen will display an alert message and automatically try to reconnect to the network;
– Increased data collection frequency: Increase the frequency of sensor readings to make the system more responsive to changes in distance;
– Measuring range limitation and data filtering: according to the actual needs of the device, the effective distance range is limited to 1~200cm, and outliers or invalid data are filtered out;
– Data smoothing: read three distance measurements each time and take their average value to reduce the measurement error and improve the stability and accuracy of the data.
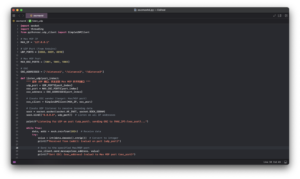
In the Python project, our goal is to receive the UDP data sent from M5StickC Plus, convert it to OSC protocol format, and finally send it to Max/MSP for subsequent processing. To do this, I wrote a Python program that listens on the local IP address (127.0.0.1) to receive the data. Since we are receiving a total of three sets of data, we set up separate UDP listening ports for each set of data, and configured the three OSC receiving ports in the Max project accordingly. In the end, all three sets of data were successfully transmitted through the local network and connected to Max.
In practice, we also encountered some technical challenges:
Unstable Wi-Fi network: Initially, we tried to connect M5StickC Plus to the mobile phone hotspot, but the connection was frequently disconnected and the communication was unstable. Later, after seeking help from our mentor, we successfully connected M5StickC Plus to the campus Wi-Fi network, which significantly improved the reliability of the connection.
Power supply problem: The M5StickC Plus has a limited built-in battery life, which makes it difficult to support prolonged operation. In order to solve this problem, we have connected a small rechargeable battery to the device, which ensures a continuous and stable power supply.
Sensor Accuracy: The common ultrasonic sensor used initially had a large error in distance measurement, which could not meet the actual needs. After replacing it with the Grove ultrasonic sensor, the measurement results became significantly more stable and accurate, effectively improving the overall reliability of the system.


